Telco Return (sometimes also referred to as TR or Telephone Return) is a system used by some cable company ISP's and satellite ISP's to provide Internet access. This system uses separate send and receive paths.
What is Telco Return?Telco return systems use two paths for the exchange of data between the user and the cable company ISP or satellite ISP:
The send path is used to send requests for data from the user via a telephone modem, such as when a user clicks on a web page link, or starts to download a file from the Internet. This does not adversely effect the performance of such systems as user requests typically consist of very small quantities of data.
The receive path, either via cable modem or satellite feed, is used to send the requested data back to the user at high-speed from the ISP, frequently in the region of 1.5mbits per second.
Since most users are receiving much more data than they are transmitting, this provides considerably faster Internet access.

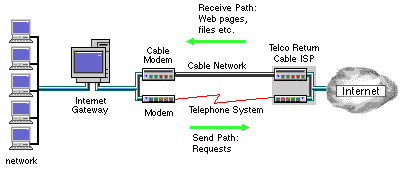
The above diagram shows a Telco Return system with a cable modem. Web pages, graphics and downloading files are received through the high-speed cable modem. The actual requests for web pages etc. are sent to the ISP via the slower telephone-based modem.
Note that the modem and cable modem are usually within a single unit, and are shown in the diagram as separate for illustration purposes only.
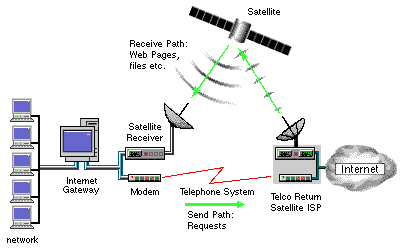
The above diagram shows a Satellite Receiver/Decoder that uses the Telco Return system. Web pages, graphics and downloading files are received through the high-speed Satellite feed from the ISP's satellite uplink. The actual requests for web pages etc. are sent to the ISP via the slower telephone-based modem.
Note that the Satellite Receiver and cable modem are usually within a single unit, and are shown in the diagram as separate for illustration purposes only.
Note that although the Telco Return system commonly uses the public telephone system and a traditional modem as the sending path, some implementations allow for this to be ISDN, leased line or other type of connection.